Slide 3 of 48
Notes:
[High Energy Astrophysics, Longair, 2nd Edition, Vol 1, p89-91]
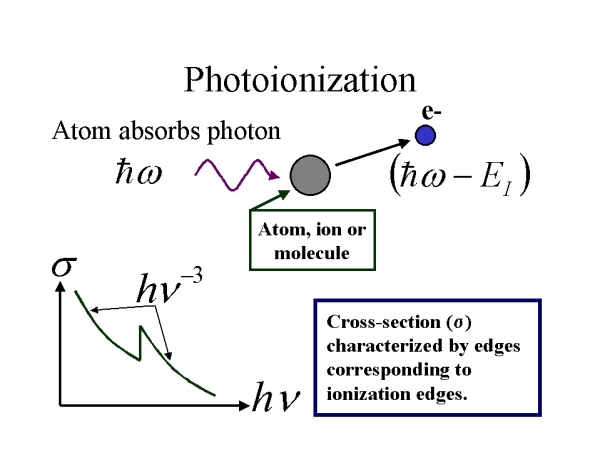
An atom, ion or molecule absorbs a photon and releases an electron with an energy equivalent to the energy of the incoming photon less the ionization energy for the level that the electron occupied.
The absorption cross-section is characterized by edges which correspond to the various ionization levels. The fall in cross-section between the edges is proportional to the cube-root of the frequency. The position of the edges in frequency space reveals which atom/ion/molecule is involved and the depth of the edge gives the amount of material in the line of sight.