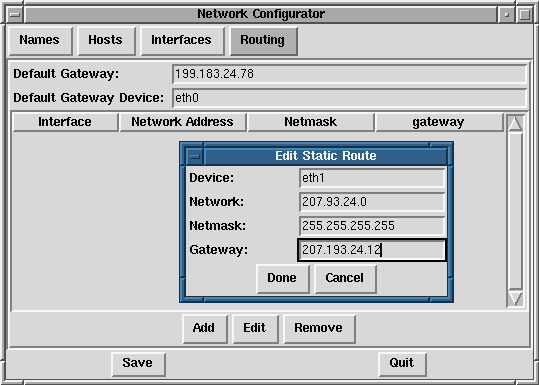
The network configuration panel shown in Figure 30 is designed to allow easy manipulation of parameters such as IP address, gateway address, and network address, as well as name servers and /etc/hosts.

Network devices can be added, removed, configured, activated,
deactivated and aliased. Ethernet,
arcnet, token ring, pocket (ATP), PPP, SLIP, PLIP and loopback devices are
supported. PPP/SLIP/PLIP support works well on most hardware, but some
hardware setups may exhibit unpredictable behavior. When using the
Network Configuration Tool click ``Save'' to write your changes to disk,
to quit without making any changes select ``Quit''.
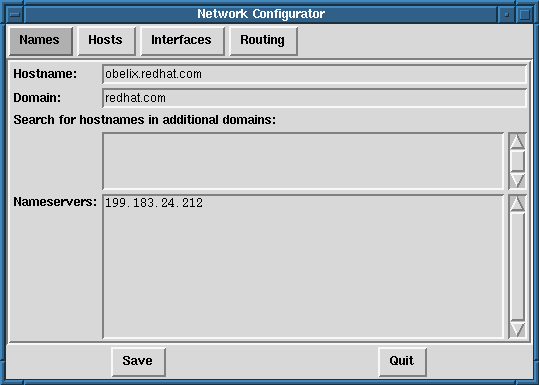
The ``Names'' panel of the Network Configuration tool serves two primary
purposes: setting the hostname and domain of the computer, and determining
which name server will be used to look up other hosts on the network. The
Network tool is not capable of configuring a machine as a nameserver.
To edit a field or add information to a field simply click on the field
with the left mouse button and type the new information.
8.4.1 Managing Names
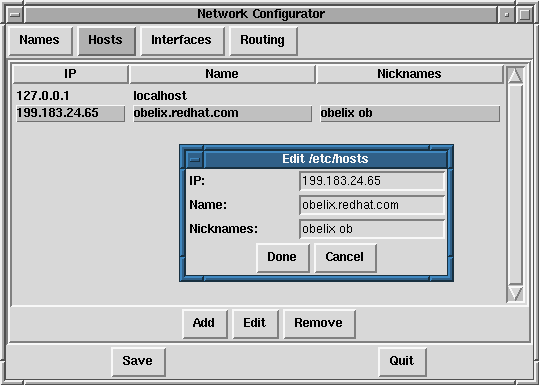
8.4.2 Managing Hosts
If you have added a networking interface to your machine since installing Red Hat Linux, or you didn't configure your ethernet card at install time, you can configure it with a few clicks of a mouse. Begin by clicking on Interfaces in the main panel. This will bring up a window of configured devices with a row of available options, see figure 32.
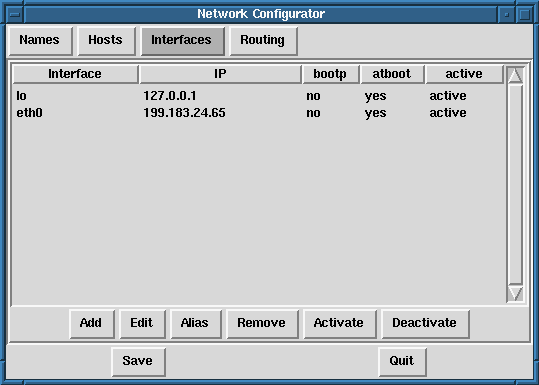
To add a device, first click the Add button then select the type of interface you want to configure from the box that appears. (Figure 33)

After providing the configuration information for your new device, click Done. The device should appear in your ``Interfaces'' list as an inactive device. (The active column should have a label of ``no''). To activate the new device highlight it with a mouse click and then click on the Activate button. If it does not come up properly, you may need to reconfigure it by clicking on Edit.