 |
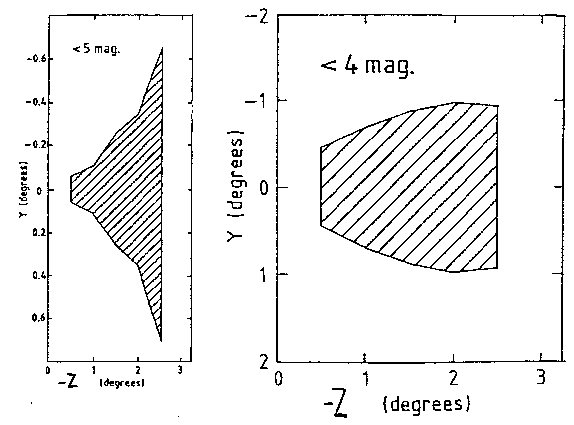
Optical light from bright sources close to a science target can enter the RGS under certain angles. To avoid contamination of RGS observations, such sources must be avoided, with approximate avoidance angles as displayed in Fig. 58. Nearby bright X-ray sources should also not be located along the dispersion direction of the RGS during an observation in order to avoid spectral overlaps. Information on how to choose a position angle in order to avoid bright sources is provided in § 4.4.
The choice of avoidance angles is entirely at the responsibility of the GO. Should an observation become too constrained due to these avoidance angles, GOs may consider violating these regions, depending on the scientific impact on the proposal.
 |